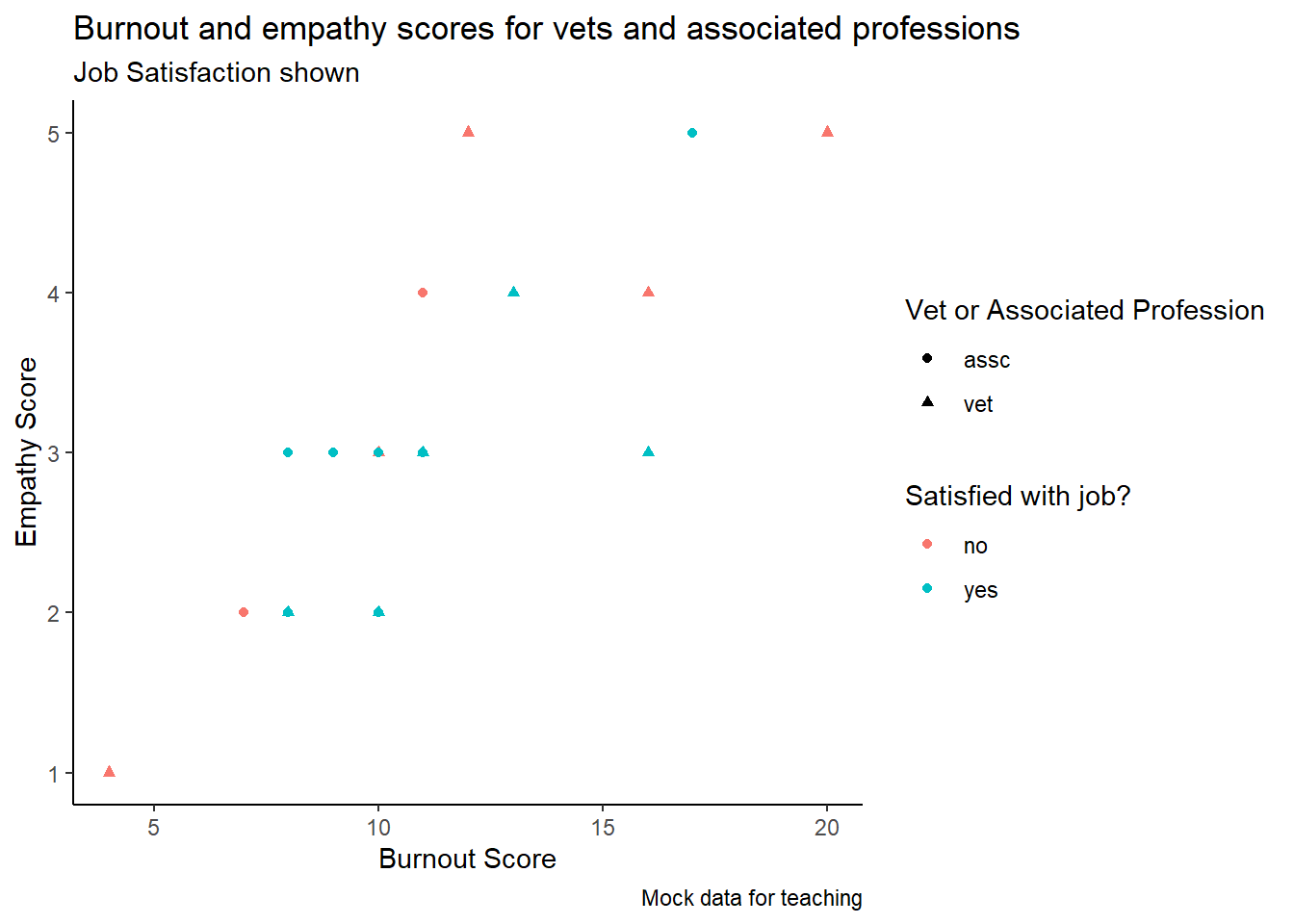
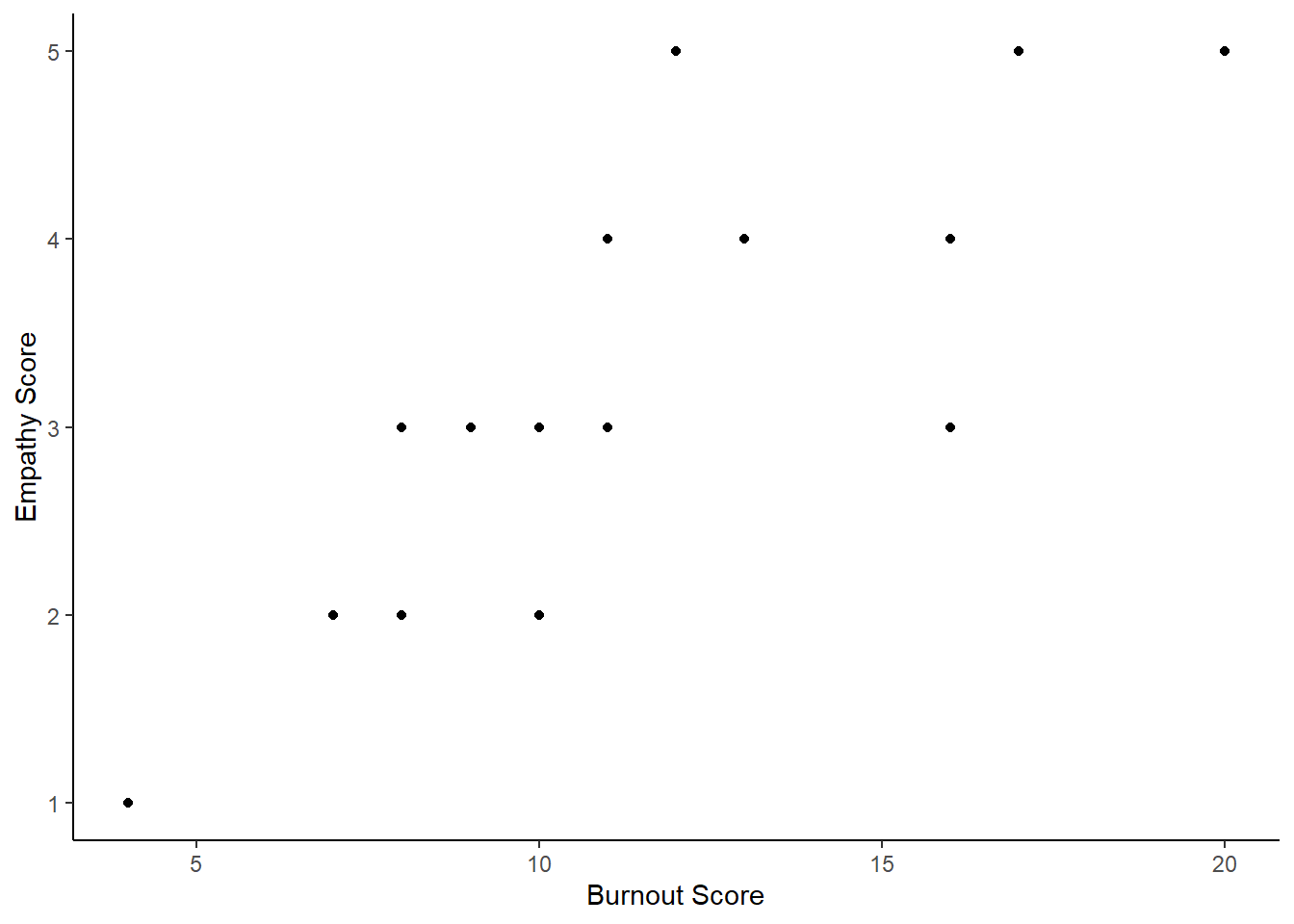
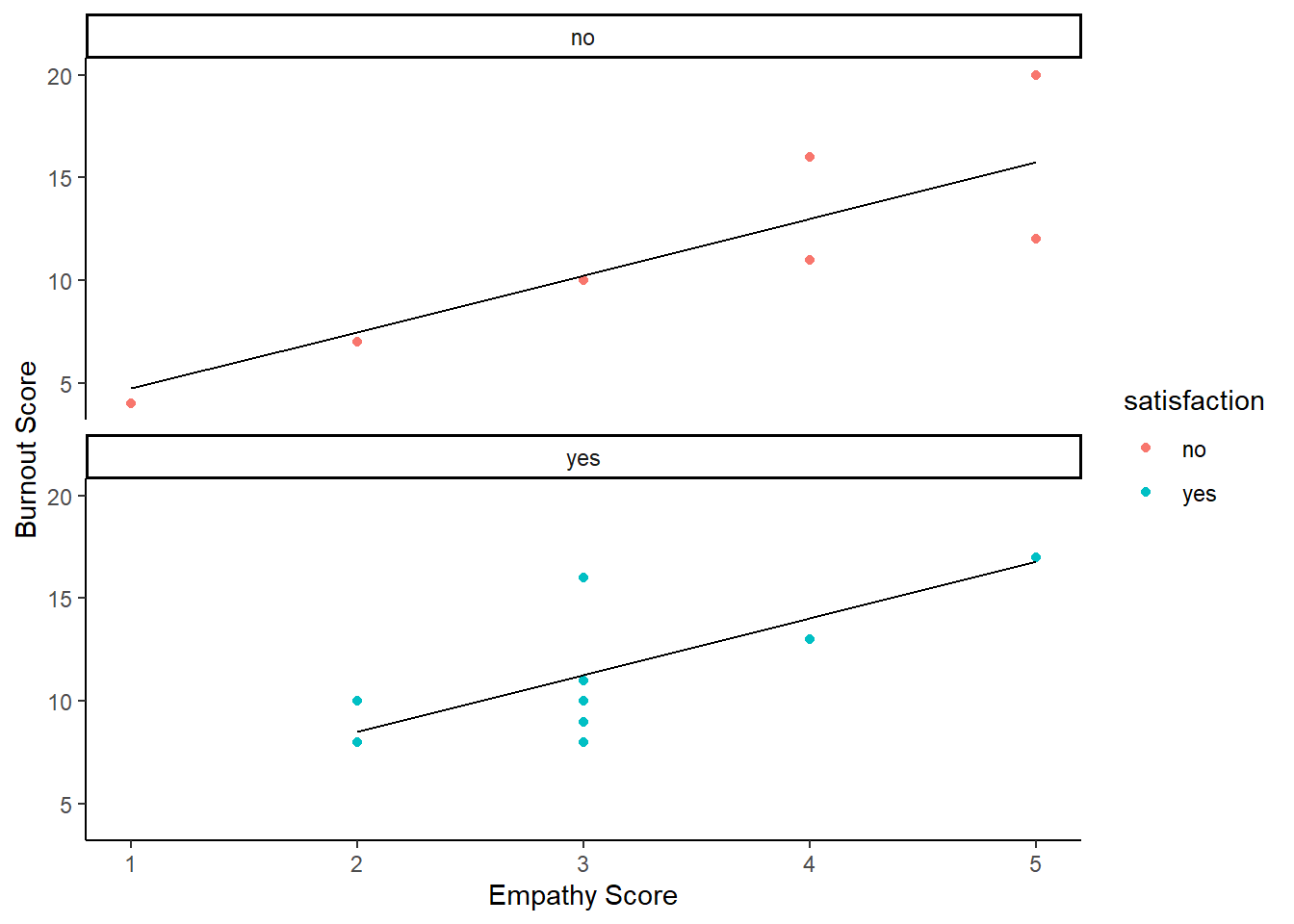
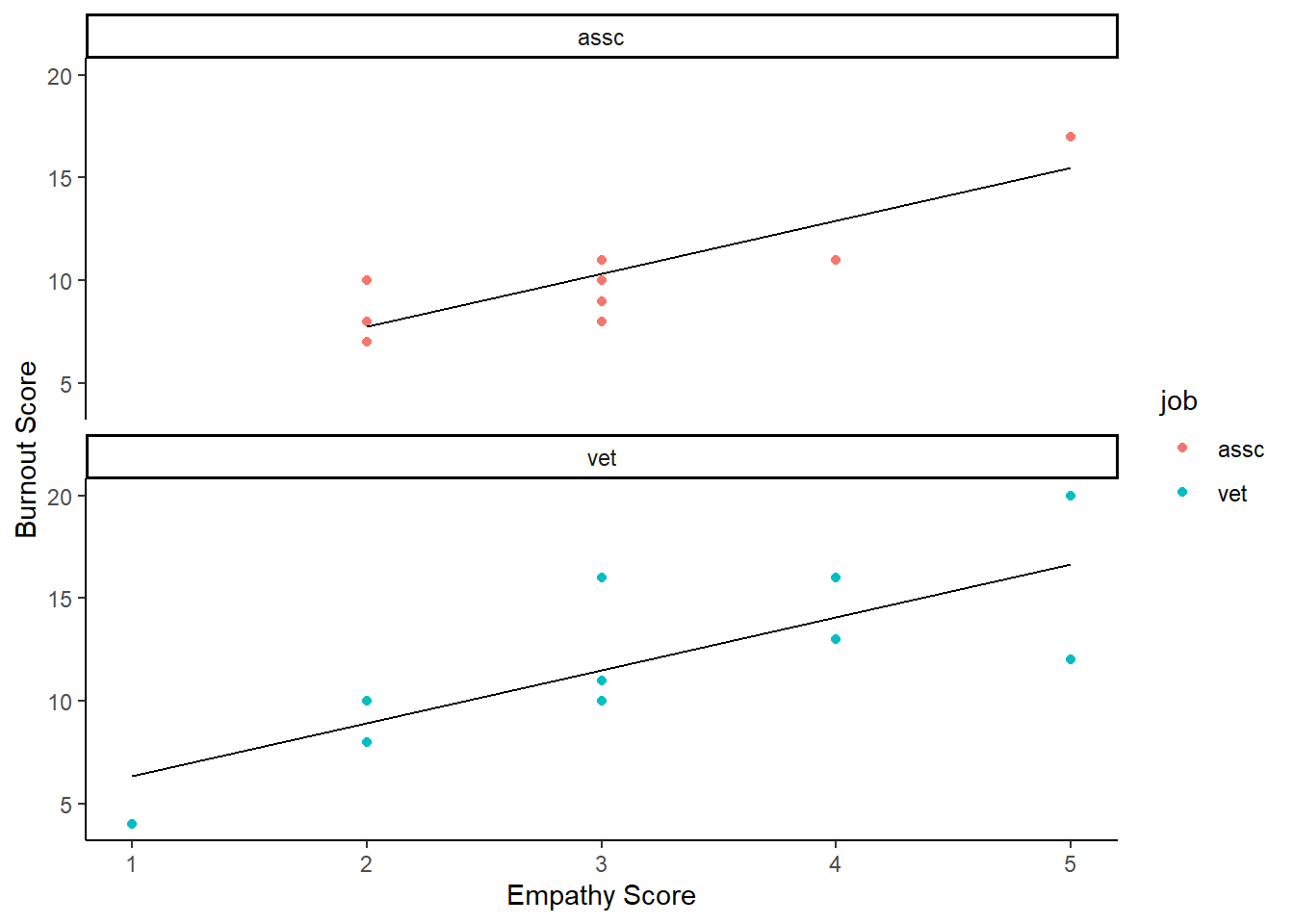
job_dat <- tibble(job = c("vet", "vet", "vet","vet", "vet", "vet", "vet", "vet", "vet", "vet",
"assc", "assc", "assc", "assc", "assc", "assc", "assc", "assc", "assc", "assc"),
burnout = c(13, 12, 4, 16, 16, 20, 8, 10, 11, 10,
10, 11, 8, 7, 8, 10, 9, 11, 17, 10),
empathy = c(4, 5, 1, 4,3, 5, 2, 3,3,2,
2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 2),
satisfaction = c("yes", "no", "no", "no", "yes", "no", "yes", "no", "yes", "yes",
"yes", "yes", "yes", "no", "yes", "yes", "yes","no", "yes", "yes"))
job_dat |>
ggplot(aes(x = burnout, y = empathy, shape = job, colour = satisfaction)) +
geom_point() +
theme_classic() +
labs(title = "Burnout and empathy scores for vets and associated professions",
subtitle = "Job Satisfaction shown",
caption = "Mock data for teaching",
x = "Burnout Score",
y = "Empathy Score") +
scale_shape_discrete(name = "Vet or Associated Profession") +
scale_color_discrete(name = "Satisfied with job?")